
adj., adj asep´tic.(See accompanying table.) medical asepsis the use of practices aimed at destroying pathological organisms after they leave the body employed in the care of patients. the absence of viable pathogenic organisms see also aseptic technique. The findings of these case studies suggest that these latex-free gloves are equal to latex gloves in terms of establishing asepsis and providing comfort and dexterity to the wearer, without presenting the risk of developing latex sensitivity and/or allergy. freedom from infection or infectious material. This article presents four case studies, in which health professionals in a perioperative setting compare the advantages and disadvantages of using traditional latex surgical gloves with those of latex-free gloves manufactured by Cardinal Health. The use of these alternative gloves has typically been limited to cases of allergy, because they have previously been associated with reduced dexterity and durability compared with latex gloves. Synthesis 6: Sterile gloves are required for surgical aseptic. There has not been sufficient evidence to ban the clinical use of latex however, in cases of suspected latex allergy, guidelines recommend the use of either latex-free gloves or powder-free, low-protein latex gloves. to be performed, risk of contamination, latex allergies and cost.
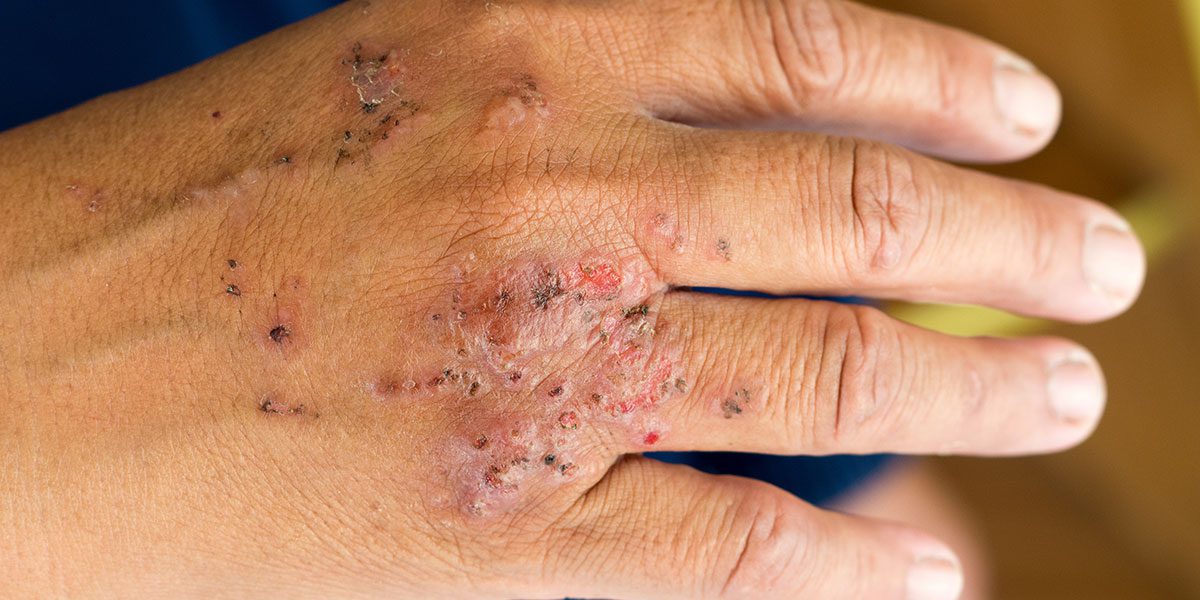

A latex allergy causes discomfort and inconvenience, and it may reduce productivity, impose significant financial burdens and even be life threatening. However, frequent use of latex gloves can lead to a hypersensitivity or allergy to latex. These gloves have traditionally been made from natural rubber latex and dusted with cornstarch powder. This is particularly important in operating theatres, where surgical site infection is a common and serious complication for perioperative patients.

Sterile protective gloves are used to reduce the risk of infection for patients and clinicians in all healthcare settings.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
